On September 30, 2021, Congress averted a potential federal government shutdown by passing a last-minute bill to fund government operations through December 3, 2021.1 Two weeks later, another measure raised the debt ceiling by just enough to sustain federal borrowing until about the same date.2 Although these bills provided temporary relief, they did not resolve the fundamental issues, and Congress will have to act again by December 3.
Spending vs. Borrowing
The budget and the debt ceiling are often considered together by Congress, but they are separate fiscal issues. The budget authorizes future spending, while the debt ceiling is a statutory limit on federal borrowing necessary to fund already authorized spending. Thus, increasing the debt ceiling does not increase government spending. But it does allow borrowing to meet increased spending authorized by Congress.
The underlying fact in this relationship between the budget and the debt ceiling is that the U.S. government runs on a deficit, and has done so every year since 2002.3 The U.S. Treasury funds the deficit by borrowing through securities such as Treasury notes, bills, and bonds. When the debt ceiling is reached, the Treasury can no longer issue securities that would put the government above the limit.
Twelve Appropriations Bills
The federal fiscal year begins on October 1, and 12 appropriations bills for various government sectors should be passed by that date to fund activities ranging from defense and national park operations to food safety and salaries for federal employees.4 These appropriations for discretionary spending account for about one-third of federal spending, with the other two-thirds, including Social Security and Medicare, prescribed by law.5
Though it would be better for federal agencies to know their operating budgets at the beginning of the fiscal year, the deadline to pass all 12 bills has not been met since FY 1997.6 This year, none of the bills had passed as of late October.7
In order to buy time for further budget negotiations, Congress typically passes a continuing resolution, which extends federal spending to a specific date based on a fixed formula. The September 30 resolution extended spending to December 3 at FY 2021 levels.8 Adding to the stakes of this year’s budget negotiations, spending caps on discretionary spending that were enacted in 2011 expired on September 30, 2021, so FY 2022 budget levels may become the baseline for future spending.9
Raising the Ceiling
A debt limit was first established in 1917 to facilitate government borrowing during World War I. Since then, the limit has been raised or suspended almost 100 times, often with little or no conflict.10 However, in recent years, it has become more contentious. In 2011, negotiations came so close to the edge that Standard & Poor’s downgraded the U.S. government credit rating.11
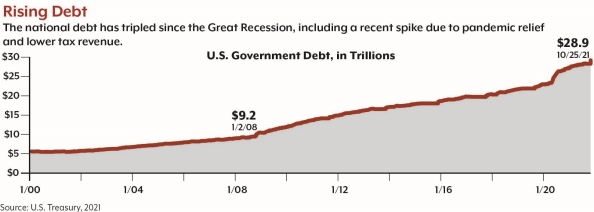
A two-year suspension expired on August 1 of this year. At that time, the federal debt was about $28.4 trillion, with large recent increases due to the $3 trillion pandemic stimulus passed with bipartisan support in 2020, as well as the 2021 American Rescue Plan and continuing effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.12-13 The Treasury funded operations after August 1 by employing certain “extraordinary measures” to maintain cash flow. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen projected that these measures would be exhausted by October 18.14
The bill signed on October 14 increased the debt ceiling by $480 billion, the amount the Treasury estimated would be necessary to pay government obligations through December 3, again using extraordinary measures. Unlike the budget extension, which is a hard deadline, the debt ceiling date is an estimate, and the Treasury may have a little breathing room.15–16
Potential Consequences
If the budget appropriations bills — or another continuing resolution — are not passed by December 3, the government will be forced to shut down unfunded operations, with the exception of some essential services. This occurred in fiscal years 2013, 2018, and 2019, with shutdowns lasting 16 days, 3 days, and 35 days, respectively. A Senate report estimated that the three shutdowns cost taxpayers almost $4 billion and nearly 57,000 years of lost production time.17
Although the consequences of a government shutdown would be serious, the economy has bounced back from previous shutdowns. By contrast, a U.S. government default would be unprecedented and could result in unpaid bills, higher interest rates, and a loss of faith in U.S. Treasury securities that would reverberate throughout the global economy. The Federal Reserve has a contingency plan that might mitigate the effects of a short-term default, but Fed Chair Jerome Powell has emphasized that the Fed could not “shield the financial markets, and the economy, and the American people from the consequences of default.”18
Given the stakes, it is unlikely that Congress will allow the government to default, but the road to raising the debt ceiling is unclear. The temporary measure was passed through a bipartisan agreement to suspend the Senate filibuster rule, which effectively requires 60 votes to move most legislation forward. However, this was a one-time exception and may not be available again. Another possibility may be to attach a provision to the education, health-care, and climate package slated to move through a complex budget reconciliation process that allows a bill to bypass the Senate filibuster. However, the reconciliation process is time-consuming, and it is not clear whether the debt ceiling would meet parliamentary requirements.19
The budget and the debt ceiling are serious issues, but Congress has always found a way to resolve them in the past. It’s generally wise to maintain a long-term investment strategy based on your goals, time frame, and risk tolerance, rather than overreacting to political conflict and any resulting market volatility.
U.S. Treasury securities are guaranteed by the federal government as to the timely payment of principal and interest. The principal value of Treasury securities fluctuates with market conditions. If not held to maturity, they could be worth more or less than the original amount paid. All investments are subject to market fluctuation, risk, and loss of principal. When sold, investments may be worth more or less than their original cost.

